
The U.S. government is canceling $500 million worth of vaccine development projects that use mRNA technology, Health and Human Services (HHS) Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr. announced on Tuesday. The decision affects 22 projects, most of which were aimed at developing vaccines for COVID-19 and seasonal flu.
The projects were funded through the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA), with proposals from major pharmaceutical companies like Pfizer, Sanofi Pasteur, and Moderna among those either rejected or withdrawn. One of the most notable cancellations was a contract with Moderna to create a bird flu vaccine, which was officially terminated in May.
According to Kennedy, the cancellations come after a review of the projects over the past few weeks. He said the decision marks a shift away from mRNA vaccine research due to concerns about its effectiveness and reliability. mRNA vaccines, which rose to prominence during the COVID-19 pandemic, work by using messenger RNA to instruct the body to produce proteins that trigger an immune response.
Kennedy argued that the technology carries more risks than benefits, particularly for respiratory viruses like COVID-19 and influenza. He claimed that mutations in these viruses can quickly make mRNA vaccines less effective. “A single mutation can make mRNA vaccines ineffective,” he stated.
However, the decision has sparked sharp criticism from public health experts. Dr. Paul Offit, a virologist at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, said the move was not based on scientific evidence and could endanger public health. Epidemiologist Dr. Michael Osterholm called it "one of the worst decisions" he’s seen in five decades of working in public health. He emphasized that traditional flu vaccine production methods are too slow in the face of a pandemic and that mRNA technology offers the speed and flexibility needed to respond quickly.
Supporters of mRNA vaccines point to their success during the pandemic. The Trump administration had invested heavily in the development of the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines, which were created faster than any previous vaccines in U.S. history. Dr. Luciana Borio, a former medical preparedness official at the National Security Council, said abandoning mRNA research in favor of older methods is a serious error.
Despite his stance, Kennedy said HHS still supports vaccines that are “safe and effective” and plans to redirect the canceled funding to broader vaccine platforms that remain useful even as viruses mutate. Critics remain concerned this decision could undermine progress made in modern vaccine development.
Health
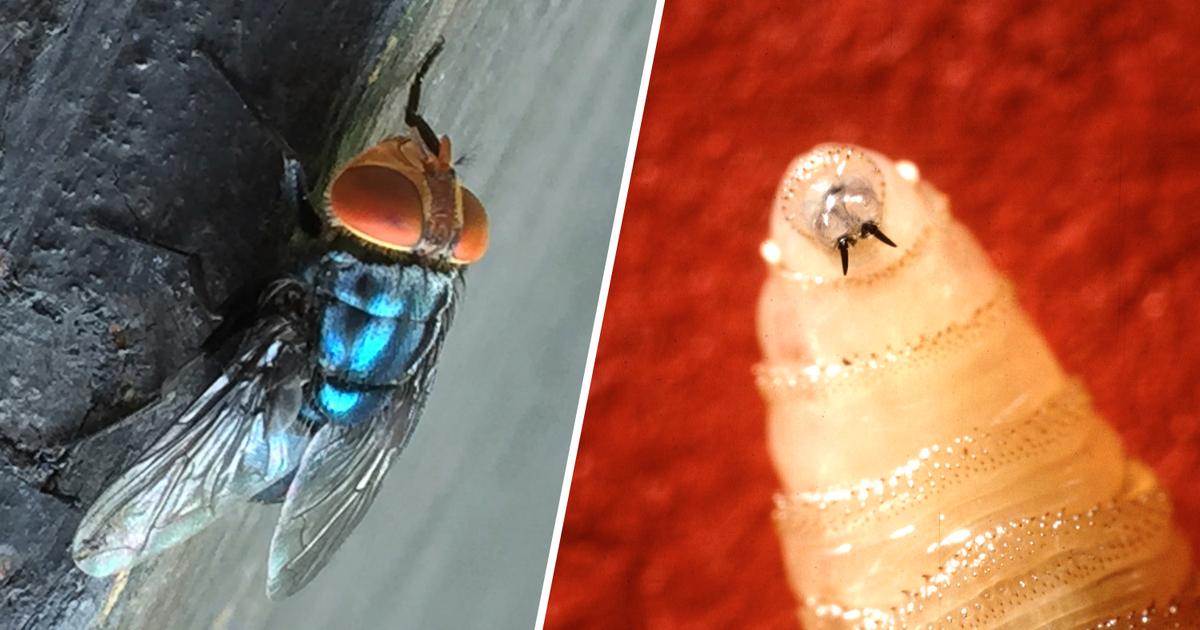

First U.S. Human Case of Travel-Linked Screwworm Confirmed by HHS
The U.S. has confirmed its first human case of New World Screwworm infestation linked to international travel, health officials announced.
Africa CDC Reports Drop in Mpox Cases, Warns of New Outbreaks
The Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC) has reported a major 58 per cent drop in mpox cases across the continent between epidemiological week 19 and week 30 of 2025.

CS Duale Suspends 40 Hospitals Over SHA Insurance Fraud
Defence Cabinet Secretary Aden Duale has suspended 40 hospitals and 12 health officials over allegations of defrauding the Social Health Authority (SHA) system.

Nigerian Nurses Suspend Strike After Talks With Government
The nationwide warning strike by Nigerian nurses and midwives has been suspended following a closed-door meeting with government officials.

Mpox Outbreak: 314 Cases and 5 Deaths Reported in 22 Counties
The Ministry of Health has confirmed 314 Mpox cases and five related deaths across 22 counties in Kenya so far.
WHO Labels Hepatitis D a Cancer Risk, Urges Global Action
The World Health Organization (WHO) has classified Hepatitis D as a cancer-causing virus, warning that it significantly increases the risk of liver cancer in people already infected with Hepatitis B.

Dei BioPharma Earns U.S. Patents for Game-Changing Therapies
In a major step forward for global healthcare, Uganda’s Dei BioPharma has secured two U.S. patents for breakthrough therapies aimed at making cancer and immune treatments more affordable and accessible.
